

University of Michigan Medical School: Michigan Medicine. Relationship between ultraviolet index (UVI) and first-, second- and third-degree sunburn using the Probit methodology. Sánchez-Pérez JF, Vicente-Agullo D, Barberá M, Castro-Rodríguez E, Cánovas M.
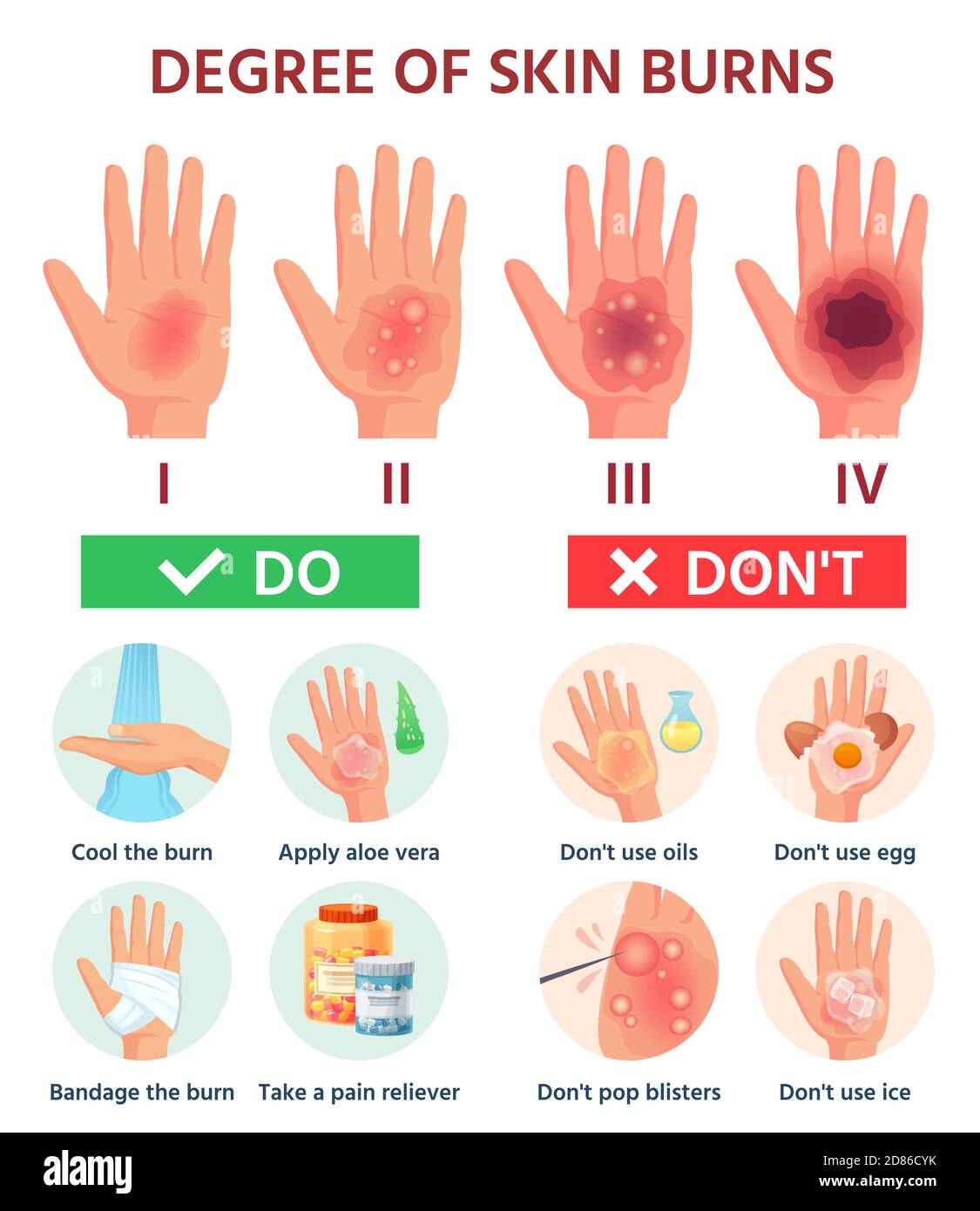
Pediatric scalds: Do cooking-related burns have a higher injury burden? J Surg Res. doi:10.4103/JCAS.JCAS_90_19īachier M, Hammond SE, Williams R, Jancelewicz T, Feliz A. Role of Burn Blister Fluid in Wound Healing. Periorbital lesions in severely burned patients. Grosu-Bularda A, Andrei MC, Mladin AD, et al. University of California San Diego School of Medicine: UC San Diego Health. Acute and perioperative care of the burn-injured patient. These burns always require medical intervention. Third-degree burns often destroy pain-sensing nerves in the lower layers of skin, which means they may not hurt very much. National Hospital Ambulatory Medical Care survey: 2015 emergency department summary tables.īittner EA, Shank E, Woodson L, Martyn JA. Third-degree burns destroy all the tissue of the epidermis and dermis, and they extend into the fatty tissue below the dermis. doi:10.1186/s1305-2Ĭenters for Disease Control and Prevention. Burn wound healing and treatment: Review and advancements. Optimal treatment of partial thickness burns in children: a systematic review. If your burn has healed, you may also be given a compression glove.Vloemans AF, Hermans MH, van der Wal MB, Liebregts J, Middelkoop E. Your therapist may bandage your hand with a stretchy bandage called ‘coban’ which helps to push the oedema out of the swollen area. You should avoid lying flat as this encourages fluid collection in your face and head which can lead to difficulty opening your eyes and may also affect your breathing. If you have facial swelling it is extremely important to maintain an upright position. Upright position (for face, head or neck burns) Please ask your therapist if you are unsure. Sometimes movement is not encouraged (e.g. Your therapist may show you specific exercises to help with this.
Muscles act as a pump, pushing fluid away from the swollen area. Slings, pillows, tables and sometimes splints may be used to position your limb.
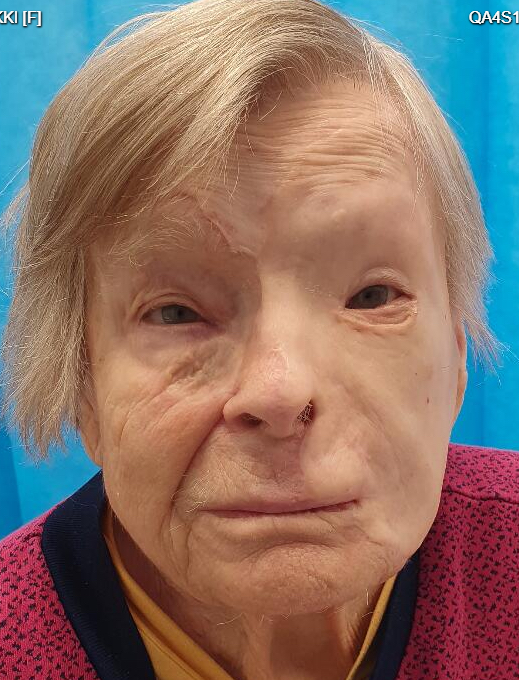
#3rd degree burn on face skin#
Third-degree and more severe burns (also called full thickness burns) damage both layers of the skin and may also damage the underlying bones, muscles, and tendons. Third-degree burns, also referred to as full thickness burns, affect all layers of skin, damaging tissue beneath the dermis. Surgery may be necessary for very deep second degree burns or those that are slow to heal. Second-degree burns involve damage to some of the second layer of skin, the dermis. It may include ointments or special dressings. The burn site appears red, blistered, and may be swollen and painful. The swollen part should be higher than the rest of the limb so that gravity can assist. Treatment for second-degree burns varies. Second-degree burns involve the epidermis and part of the dermis layer of skin. ElevationĮlevation will encourage drainage of fluid and allow it to be reabsorbed by the body. There are steps that you can take to reduce the amount of swelling you have and to prevent it from getting worse. In this instance it is even more important to follow the advice below to minimise the negative effects of fluid. If you have had a skin graft, tissue fluid and bleeding can affect the healing and in some cases, may cause the graft to fail. Otherwise it can increase pain, make it difficult to move, cause stiffness or deformity of joints, interfere with the normal functioning of your muscles, nerves and blood vessels and can cause a superficial burn to deepen. It is very important that the swelling is reduced as soon as possible. The extent and location of the swelling will depend on how the burn was caused and the location and depth of the burn injury. 2) Tissue sparing debridement was then done. Meanwhile use local antimicrobial cream ( silversulfadiazine). Third degree burn of face Third degree burn of head ICD-10-CM T20.30XA is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group(s) (MS-DRG v 40. Swelling tends to occur soon after injury and generally decreases after 48–72 hours, although this timescale can vary. 1) Waited for 3 days to observe the final depth of the burn, Fig. The swelling is caused by fluid leaking from blood vessels and collecting around damaged areas. For example, if your burn is on your arm, then your hand can also become swollen, due to the effects of gravity. Why do I have oedema?ĭepending on the size of the burn, you may experience swelling immediately around the injured area or it may involve other parts of the body.
#3rd degree burn on face how to#
This leaflet will help you understand why you may have oedema following your burn injury and give you some advice about how to reduce swelling and prevent complications. Oedema is the medical name for ‘swelling’.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
